It seems that the European Commission wants to change how its Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) is run. Or at least how it’s marketed. From the BBC:
EU plans CAP reforms for ‘greener’ farm subsidies
The European Union has announced plans to reform its Common Agricultural Policy – its most expensive scheme, and one of the most controversial. The CAP cost 58bn euros (£51bn; $80bn) last year – 47% of the whole EU budget.
The European Commission does not want to cut the budget, but change its priorities – including linking direct payments to environmental measures.
I find this fascinating, for a couple of reasons. First, amidst all of the current discussion about the merits of additional fiscal federalism in the EU — i.e. whether increasing the independent taxation and spending power of the EU might be the best way to deal with the ongoing eurozone crisis — this serves as an important reminder of the current state of affairs in that regard. The EU does have its own budget, and does get to spend money on EU-wide priorities. The problem is that its budget is very small: only about €140 billion in 2011 for the entire 500 million people in the EU — roughly the same as government spending in Denmark alone (population 5 million). And of that tiny budget, almost half is devoted to agricultural subsidies.
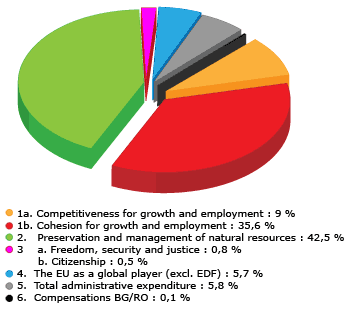 Given such a small budget to begin with, it has always seemed very odd that so much of it is consumed by subsidies to farmers. And the EU is apparently a bit self-conscious about that fact: farm subsidies are described as spending for the “preservation and management of natural resources” in the EU’s budget planning documents. (Note the reassuring green color on the pie chart.) And they rather defensively note in their FAQs that the share of the EU’s budget that has been devoted to farm subsidies has been steadily falling.
Given such a small budget to begin with, it has always seemed very odd that so much of it is consumed by subsidies to farmers. And the EU is apparently a bit self-conscious about that fact: farm subsidies are described as spending for the “preservation and management of natural resources” in the EU’s budget planning documents. (Note the reassuring green color on the pie chart.) And they rather defensively note in their FAQs that the share of the EU’s budget that has been devoted to farm subsidies has been steadily falling.
Why have such large agricultural subsidies, then? There are several possible explanations, but I think that there are two that are the most important. First, they served as an important lubricant in the political process of getting everyone on board with the EU project. As economists say, they were an important side-payment made from some members of the EU to others to faciliate other agreements.
Second, I think it’s reasonable to believe that there’s a genuine value placed by many Europeans and their governments on farming villages, lifestyles, and countrysides. In other words, I think that many non-farmers in Europe reap positive externalities from the existence of their farming communities. So for better or worse, they’re willing to pay subsidies to maintain them.
But that doesn’t mean that the EU can’t try to do a better job of marketing them. And I think that’s what’s going on here; the EU realizes that if it more explicitly ties these farm subsidies to environmental protection, they will be more defensible. And they’re probably right. So whether you like this idea or not will probably depend largely on what you think “environmental protection” is really all about.



Leave a Reply