Probably the most important debate on U.S. monetary policy is whether there really is an aggregate demand shortfall and, as a result, a negative output gap. If the answer is yes, then the Fed should be doing more. If no, then monetary policy should show restraint. Some Fed officials like St. Louis Fed President James Bullard and Minneapolis Fed President Narayana Kocherlakota believe there is no significant aggregate demand or domestic output gap problem and thus want to tighten monetary policy soon. Fed chairman Ben Bernanke, on the other hand, believes there is still ample slack in resource markets and is open to further monetary stimulus. And then there are the Market Monetarists and other like-minded commentators in the blogosphere who think there is a significant aggregate demand problems since the Fed has been effectively tight since mid-2008. Who is right?
The answer has always been clear to me. But for those still unsure let me direct you to some evidence that makes a very convincing case that there has been and continues to be an serious aggregate demand shortfall. The evidence comes from the NFIB’s survey of Small Business Economic Trends. This survey, among other things, provides a question to the small firms of this nation that is relevant to this debate: “What is the single most important problem facing your firm?” There are nine answers firms can choose, but below I focus on just four of them and their recent trends:
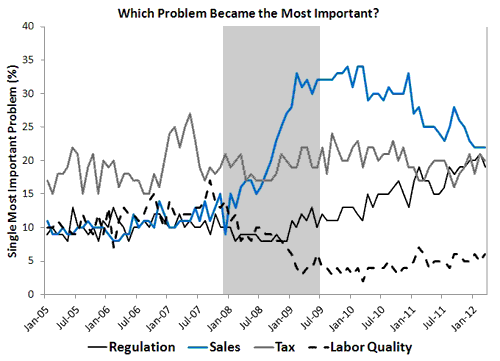
The first thing to note from this figure is that concerns about sales or demand became the most important problem. It alone explodes in 2008. Regulation, taxes, and labor quality (sorry Kocherlakota , no labor market mismatch problems here) did not sharply intensify. Labor quality concerns actually fall and though regulation eventually starts to gradually rise, concerns about demand were and continue to be the foremost among small firms.
There is more to the poor sales data. It closely tracks the unemployment rate and the output gap as seen below. These findings undermine Kocherlakota and Bullard’s claims that the CBO’s output gap is overstated. For if the output gap were truly smaller and there were no serious aggregate demand shortfall, then one would not expect to see the relationships below.

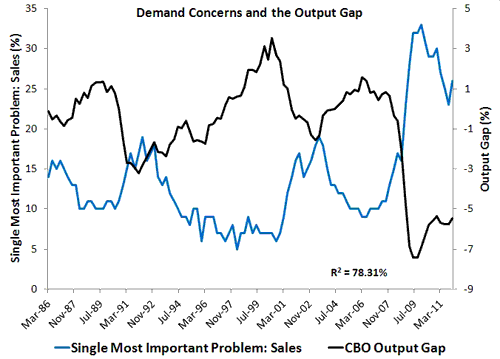
This evidence in conjunction with that of downward wage rigidity, excess money demand, and the Fed handling the housing recession just fine for two years should remove any doubt about there an aggregate demand problem. The real debate is how best to respond to this problem.
P.S. See Mike Konczal’s earlier post using the NFIB data.



Leave a Reply