No matter how you cut the April report on consumer prices, retail inflation keeps coming up zero. Here are the key points:
- The consumer price index (CPI) fell a tiny bit in April but has remained essentially unchanged since January.
- The core CPI (excluding food and energy) hasn’t posted a significant increase dating back to last October, and its 0.9 percent rise from a year ago is its smallest 12-month increase since 1966.
- The Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland’s median CPI continued a trend of essentially no change since October and is up a mere 0.5 percent from a year ago—a new year-over-year low for the series.
Oh, and the sticky-price CPI was up only 1.25 percent (annualized) in April. Maybe we ought to explain this last one a little more.
When you look at the headline CPI, what you’re really looking at is a constellation of price movements that are a mixture of various forces. For example, there are changes in market conditions that are specific to particular goods—dairy prices fell sharply in April, presumably in response to an unanticipated jump in milk production. Stripping away these idiosyncratic price movements is, in large part, what the core inflation measures, including the Cleveland Fed’s median CPI, are designed to do.
But economists tend to think of two general forces that drive all prices: (1) the amount of “slack” in the economy influencing the pricing power of firms and workers and (2) inflation expectations, which affect forward-looking price and wage decisions.
Of course, these two forces are unlikely to affect all prices in the exactly same way. Economists have long accepted the idea that some prices are “sticky,” meaning they may not be particularly sensitive to changing market conditions, including economic slack. But if these sticky prices are, in fact, insulated from the ups and downs of the marketplace, might they be more forward looking?
In recent work, we used data on the price flexibility of specific goods to separate the CPI into two components: a flexible-price CPI and a sticky-price CPI. What we found was that flexible-price goods represent roughly 30 percent of the CPI market basket, and these goods tend to respond to the state of the economy. However, the sticky-price goods that make up the remaining 70 percent of the CPI market basket don’t appear to respond to economic conditions. Consider the figure below, which shows the correspondence between the flexible-price CPI and the sticky-price CPI to the amount of slack in U.S. labor markets—the so-called Phillips curve relationship.
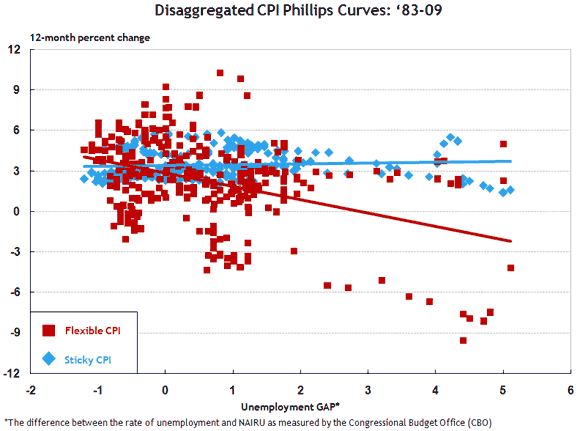
But what the sticky-price CPI lacks in responsiveness to the economy, it seems to make up in terms of its ability to capture inflation expectations. In other words, the sticky-price CPI seems to be more forward looking.
What does all this have to do with the April CPI report? Well, not any more than you already know; this most recent CPI report doesn’t have a hint of inflation in it. The flexible-price portion of the CPI that seems most responsive to the state of the economy fell last month, as it has, on average, during the past three months (–0.7 percent on a core basis.) And the sticky-price part of the CPI that seems to be most forward looking is only limping ahead, up 1.25 percent in April, and is less than 1 percent on a year-over-year basis.
By the way, if you want access to these data back to 1967, we’ve made them available to you on the Atlanta Fed’s Inflation Project.


Leave a Reply