The last employment numbers provide yet another disappointing bit of news for millions of households all around the country. No net employment gain. However, I am afraid that this is only the very tip of the iceberg because a long-term view shows a much bleaker picture.
Figure 1 shows how long it took for the employment level to return to its peak level after a recession, and how much job loss occurred relative to that peak. The employment numbers exclude people that were employed in the WPA, NYA and CCC, and focuses on individuals employed in nonfarm activities.
During the Great Depression, the employment level declined for 4 years and almost 10 million jobs were lost compared to the peak employment level that prevailed in August 1929. It took 136 months (over 11 years) to return to this level of employment, but, without the avoidable 1937 recession, the full recovery would have occurred after 102 months (8.5 years) if one takes the trend of recovery that prevailed from 1933.
The Great Recession led to a loss of almost 9 million jobs compared to the peak employment level of January 2008. The loss of jobs occurred at a faster rate than the Great Depression but employment recovered sooner and started to rise after 2 years. However, once the employment recovery started, it occurred at a slower rate than during the Great Depression. If the recovery continues at the same pace, AND assuming that no recession occurs during the recovery phase, it will take about 9 years to return to the employment level of January 2008. Thus, given everything else, it will take longer for employment to fully recover than during the years prior to the 1937 recessions.
The picture is even bleaker today if one included New Deal employment programs. Figure 2 shows that those programs allowed employment to recover fully after 80 month (less than 7 years) and only three years after the New Deal Programs were implemented. The timid Bush and Obama stimulus have barely made a dent in the employment problem over the past two years.
This, once again, suggest a powerful employment policy to help the economy. Instead of concentrating its efforts on tax rebates and bailing out banks, and waiting for them to lend to businesses, the federal government should directly hire people and involve them is activity that benefited the entire country. We do not need a temporary stimulus; we need a permanent institutionalized and decentralized government program that hires anybody willing to work and unable to find a job in the private sector. By sustaining income and the productivity of workers, a government employment program would tremendously helps to sustain the employability of workers and would improve the confidence of private business, which would in turn improve private employment.
Figure 1. Difference between peak employment level and current employment level. Nonfarm payroll employment, seasonally adjusted, millions of people.
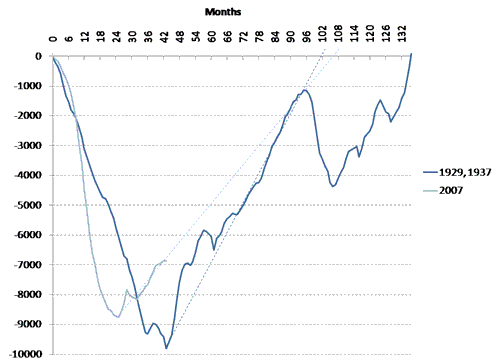
Sources: BLS (Current Employment Survey), Federal Reserve Bulletin (June and September 1941).
Note: People employed in the WPA, NYA and CCC are not included.
Figure 2. Same as Figure 1 with New Deal Federal Employment Programs.
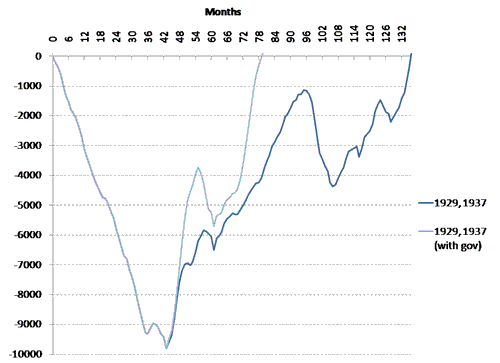
Sources: Federal Reserve Bulletin, Social Security Bulletin.



Leave a Reply