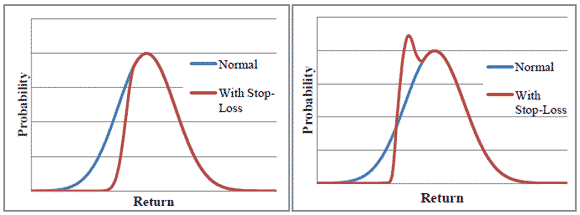
I’m sure everyone has been presented with the following logic: put in a ‘stop-loss’ at some arbitrary amount, say losing 1%. Then, your payoff distribution is tilted towards infinity, as shown above. It’s like the idea of going to Vegas, and saying you will stop when you lose $500, so you think that you still have an equal chance of generating those +$500 and up numbers, and the bad outcomes are just truncated at -$500. Alas, it doesn’t work like the graphs above. Instead, it generates the graph below, with a lot of probability mass at the stop-loss point:
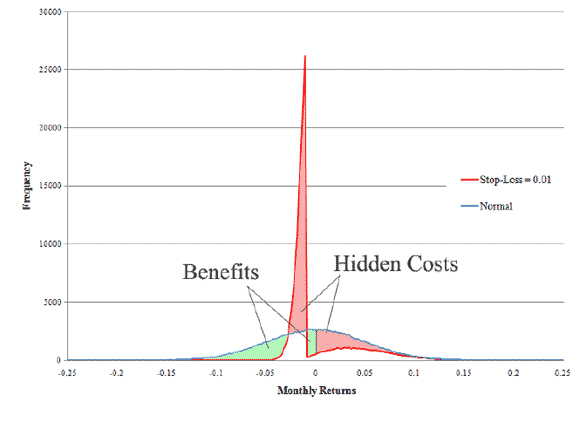
From a nice little paper by Detko, Ma and Morito (2008).


Leave a Reply