Earlier I displayed some data on output and factor usage in the manufacturing and home construction industries. Those were clearly cases of lack of demand: people wanted to buy less of those items, so suppliers produced less of them and used less capital and labor in the process. It’s no surprise that, say, a 20 percent reduction in what customers purchase would reduce usage of labor and capital by about 20 percent.
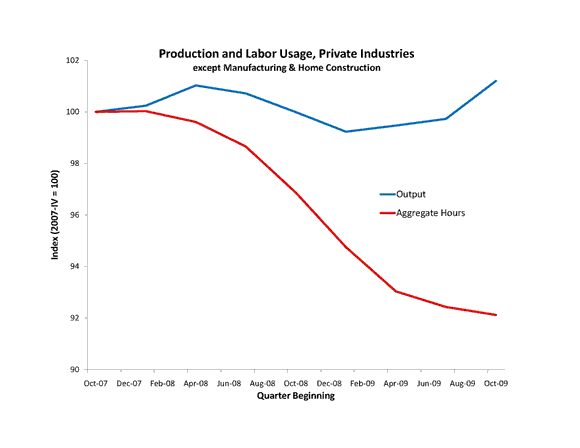
Manufacturing and home construction together were only about 15 percent of the overall private sector, so it worthwhile to look at the rest of the private sector industries. The chart below shows that rest of the industries are STILL PRODUCING at pre-recession levels. Unlike the home construction and manufacturing industries, these industries cannot (on average) blame their drastic labor cuts on a lack of production: they are still producing and earning real incomes like before, but have decided to do so with a much smaller workforce.
Disclaimer: This page contains affiliate links. If you choose to make a purchase after clicking a link, we may receive a commission at no additional cost to you. Thank you for your support!



Leave a Reply