I have been reading a lot lately about the role of small firms in the economy. Recommended resources in this regard include these Kauffman Foundation papers.
One of the themes emerging from this literature is that focusing just on firm size misses an important aspect of job creation and destruction in the U.S. economy—namely, the interaction between firm size and firm age. To illustrate this, the following chart is a dissection of the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) quarterly Business Employment Dynamics (BED) data into private employer firms with fewer than 50 employees and those with at least 50 employees (note that the BED classifies businesses using a dynamic size measure in which the job creation/destruction is allocated to a size class dynamically as a business moves through a size class from prior quarter to the current quarter). Within each firm type it is possible to allocate net employment change accounted for by opening firms (firms that had zero employment in the previous quarter), closing firms (firms with zero employment this quarter), and the net job change at surviving firms (employment at firms that expanded over the quarter less employment at firms that downsized over the quarter).
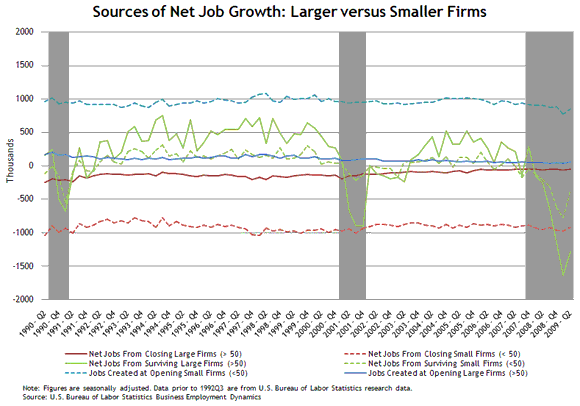
This chart displays some striking features:
- The contribution of opening small firms to net job growth is very large (averaging about 1 million jobs a quarter). In fact, when opening firms are netted out of the data, existing firms on average destroy more jobs than they create.
- Job creation at new firms has been relatively stable over time. During the recessionary period from the end of 2007 through the second quarter of 2009, the decline in jobs created at opening firms was surprisingly small.
- Job losses at closing firms did not surge in the most recent recession. In fact, job destruction caused by closing firms is relatively stable over time (research suggests that, in addition to the fact that many firms get smaller before they finally close, there is a significant “up or out” phenomenon in that many firms that closed were recently opened firms that failed).
- Most of the cyclical action is at surviving firms, and larger surviving firms tend to account for most of the variation in net employment change. During the recessionary period from the end of 2007 through the second quarter of 2009, surviving firms with at least 50 employees lost about twice as many jobs as firms with fewer than 50 employees (see for example, the study by Moscarrini and Postel-Vinay on the relative cyclical sensitivity of large and small firms).
Of course, this is largely an accounting exercise. The challenge is trying to understand the causes for these features, and how they may change over time. It seems that there is much we don’t know about the underlying factors. For instance, this paper by Dane Stangler and Paul Kedrosky investigates in considerable detail the possible explanations for why the number of new firms is so stable over time. In the end, the phenomenon remains largely a puzzle, and there are many subplots. For instance, the correlation between venture capital spending and overall firm creation is negligible but very important in high-tech industries. Also, the dramatic increase over time in the number of entrepreneurship courses offered at colleges and universities had no appreciable impact on the number of new firms in the United States (although it may have prevented a decline).
Perhaps the focus on the number of new firms is misguided. What really matters might be who these new firms are—not how many there are. Research by Dane Stangler suggests that, at any point in time, a relative handful of high-performing companies account for a large share of job creation and innovation. This conclusion suggests that a key to long-term economic growth may lie in ensuring that the economic environment is conducive to the ongoing creation of these types of high-growth performers.
Disclaimer: This page contains affiliate links. If you choose to make a purchase after clicking a link, we may receive a commission at no additional cost to you. Thank you for your support!



Leave a Reply