As Dave Altig, Atlanta Fed research director, pointed out earlier this week in this blog post, there is a great deal of interest these days in the labor force participation rate—particularly its level and the direction it’s going. The question that seems to be on everyone’s mind is how many of the nonparticipants in the labor force can we expect to return to the market. The answer to this question has immediate implications for the unemployment rate (especially if all these nonparticipants were to return to unemployment rolls), and longer-term implications for economic growth—our economy needs workers to fuel production.
The analyses that I can find to date are all primarily focused on a statistical detangling of demographic versus behavioral changes, structural versus cyclical changes, and employment trend versus employment gap debates. But all of this discussion begs the question that my colleague, Melinda Pitts, and I have been investigating: What are these labor force nonparticipants doing? Perhaps an answer to that question will help us get a better handle on which nonparticipants are likely to return to the labor force in the near future.
The Current Population Survey (CPS), administered by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), asks labor force nonparticipants about their reason for absence (details of the CPS questionnaire are available from the NBER). The reason given by nonparticipants that gets most of the attention is “discouraged over job prospects.” In April 2012, these people accounted for only 1.1 percent of all nonparticipants (41 percent of the marginally attached—those who want a job, are available to work, and searched in the previous year). The vast majority of nonparticipants are absent because of retirement, disability, going to school, caring for household members, or other reasons.
Using the latest survey data we have available (November 2011), we find that most nonparticipants are retired (48 percent); the share who are in school, disabled, or taking care of household members are 18 percent, 16 percent, and 15 percent, respectively; and the share in the category termed “Other” comes in at about 2 percent.
For purposes of better understanding the decline in labor force participation, however, we look at the reasons for absence given by people who leave the labor force. Those who have left the labor force are arguably more likely to return (depending on the reason, of course) than those who have never been in the labor force. A feature of the CPS allows us to track certain individuals from one year to the next, so we are able to identify people who leave the labor force. Chart 1 illustrates how individuals who are not in the labor force—but who were employed or unemployed the previous year—are distributed across the reasons for nonparticipation. The raw data are not seasonally adjusted, of course, so we plot the numbers as a 12-month moving average—this approach does not affect the overall observed trends in the data. In addition, we restrict our analysis here to those between the ages of 25 and 54, since retirement overwhelmingly dominates the nonparticipation decisions of older workers, and schooling dominates the nonparticipation decisions of younger workers.
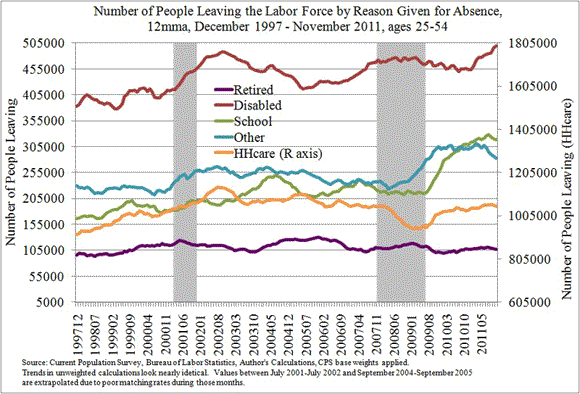
Chart 1 illustrates what the labor force participation rates have been telling us. For every reason given for absence, except perhaps “Retired,” the number of people leaving the labor force has increased during or after the recession of 2008. The most dramatic increases are seen among those people giving “School” and “Other” as a reason. However, since we are in search of changes in reasons that might be out of the ordinary, especially any significant upward shifts in nonparticipants giving a particular reason during and after the recession, we also look at how these folks leaving the labor force are distributed across the different reasons. This information will tell us whether the number of people giving one particular reason increased disproportionately compared with the other reasons.
Chart 2 plots the shares of all of those leaving the labor force (ages 25–54) giving each reason for their absence. Since the beginning of the recession, there has been a significant shift toward the reasons of “School” and “Other” among nonparticipants who have left the labor force within the previous year. The share levels attained by the reasons of “School” and “Other” are historically unprecedented by the end of the data series. These shifts also appear to have come mostly from a decline in the share of people leaving the workforce to take care of household members (HHcare). This is evidenced through the dramatic drop in the share giving the “HHcare” reason at the same time.
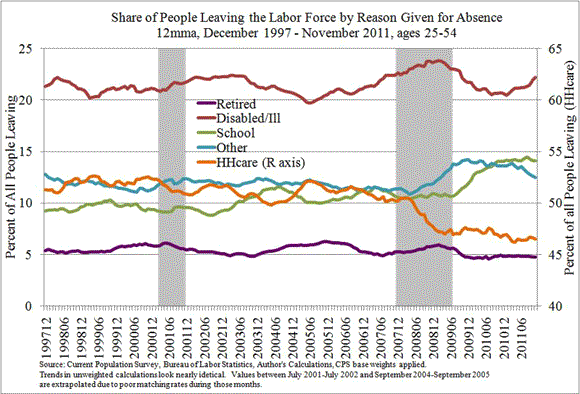
It is difficult to interpret the implications of the rise in share of “Other” as a reason for nonparticipation among those leaving the labor force, although this category may be capturing some of the discouraged workers. The implication for the rise in “School” is unmistakable, however. With reasonable expectations, these individuals should re-enter the labor force with enhanced—or at least better-aligned—skills that will be able to make a positive contribution to overall economic growth.



Leave a Reply