
As as sports fan, watching Brady and Belichick win the Super Bowl, Roger Federer triumph at the Australian Open and LeBron James carry the Cleveland Cavaliers to victory over the Warriors, it struck me how we take uncommon brilliance for granted. It is so easy, in the moment, to find fault, as many have, with these superstars and miss how special they are. That was the same reaction that I had as I watched another earnings report from Apple Inc (NASDAQ:AAPL) and the usual mix of reactions to it, some ho hum that the company made only $45 billion last year, some relieved that the company was able to post a 3% growth rate in revenues and the usual breast beating from those who found fault with it for not delivering another earth-shaking disruption. Since this is a company that I have valued after every quarterly earnings report since 2010, I thought this would be a good time to both take stock of what the company has managed to do over the last decade and to value it, given where it stands today.
The Cash Machine Revs up
In my last post on dividend payout and cash return globally, I noted that large cash balances don’t happen by accident but are a direct result of companies paying out less than they have available as potential dividends or free cash flows to equity, year after year. Since Apple’s cash balance almost reached $250 billion in its most recent quarterly report, by far the largest cash balance ever accumulated by a publicly traded company, I decided that the place to start was by looking at how it got to its current level. I started by collecting the operating, debt financing and reinvestment cash flows each year from 2007 to 2016 and computing a free cash flow to equity (or potential dividend) each year.
(click to enlarge)
Starting in 2013, when Apple started to tap into its debt capacity, the company has been able to add to its potential dividends each year. In 2015 alone, Apple generated $93.6 billion in FCFE or potential dividends, an astounding amount, larger that the GDP of half the countries in the world in 2015. Each year, I also looked at how much Apple has returned to stockholders in the form of dividends and stock buybacks.
(click to enlarge)
Note that while Apple took a while to start returning cash, and it needed prompting from David Einhorn and Carl Icahn, it not only initiated dividends in 2012 but has supplemented those dividends with stock buybacks of increasing magnitude each year. In fact, Apple returned $183 billion in cash to stockholders in the last five years, making it, by far, the largest cash-returner in the world over that period.
There are two amazing (at least to me) aspects to this story. The first is that in spite of the immense amounts of cash that Apple has returned each year, its cash balance has increased each year, partly because its operating cash flows are so high and partly because they are being supplemented by debt payments. You can see the cash build up between 2007 and 2016 in the chart below:
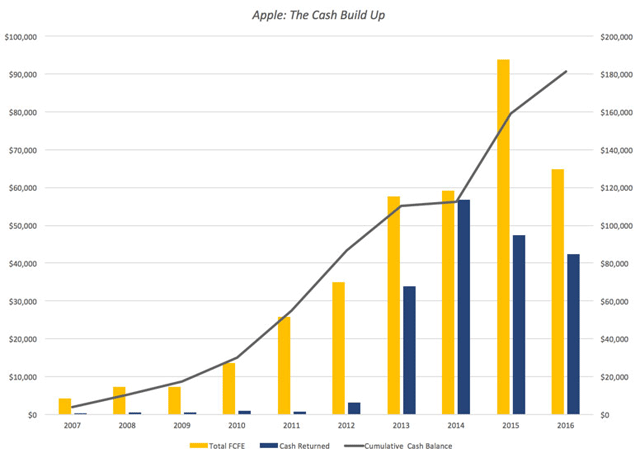
Note that while Apple was returning $183 billion in cash between 2013-2016, its cash balance continued to increase, as its cash inflows increased even more. If having a cash spigot that never turns off is a problem, Apple has it, but I am sure that it will not get about as much sympathy from the rest of the world as a supermodel who complains that she cannot put on weight, no matter how much she eats. The other equally surprising feature of this story is that Apple’s managers have not felt the urge (yet) to use their huge cash reserves to buy a company, a whole set of companies or even an entire country, a fact that those who like Apple will attribute to the discipline of its management and Apple haters will argue is due to a lack of imagination.
My Apple Valuation History
As many of you who have been reading this blog are aware, I have valued Apple many times before but rather than rehash old history, let me summarize. For Apple, the story that I have been telling about the company for the last five years has been remarkably unchanged. In my July 2012 valuation, where I looked at Apple just after it had become the largest market cap company in the world and had come off perhaps the greatest decade of disruption of any company in history (iTunes, iPod, iPhone and iPad), I concluded that while Apple was one of the great cash machines of all time, its days of disruption were behind it, partly because Steve Jobs was no longer at the helm but mostly because of its size; it is so much more difficult for a $600 billion company to create a significant enough disruption to change the trend lines on earnings, cash flows and value.
So, in my story, I saw Apple continuing to produce cash flows, with low revenue growth and gradually decreasing margins, as the smartphone business became more competitive. I won’t make you read all of the posts that I have on Apple, but let me start with a post that I had in August 2015, when I updated the Apple story (and looked at Facebook and Twitter at the same time). The value I estimated for Apple in that post was $130, higher than the stock price of $110 at the time, prompting me to buy the stock. I revisited the story after an earnings report from Apple in February 2016 and compared it to Alphabet. At the time, I valued Apple at about $126 per share, well above the $94/share that it was trading at the time. In May 2016, Carl Icahn, a long time bull on Apple sold his shares, and Warren Buffett, a long time avoider of tech companies, bought shares in the company. In a post at the time, I argued that while these big names entering and exiting the stock may have pricing consequences, I saw no reason to change my story and thus my value, leaving my Apple holdings intact.
Apple’s Earnings Report & My Narrative
Last week, Apple released its latest 10Q and in conjunction with its latest 10K (Apple’s fiscal year end is in September). It contained a modicum of good news, insofar as there was growth in revenues as opposed to the decline posted in the prior quarter and still-solid profit margins, but the revenue growth was only 3% and the margins are still lower than they used to be. Using the numbers in the most recent report, I took at look at my Apple story and guess what? It looks just like it did last year, a great cash machine, with very slow-growing revenues and declining margins. Using the process that I describe, perhaps in too much detail in my book on narrative and numbers, I converted my story in inputs to my valuation:
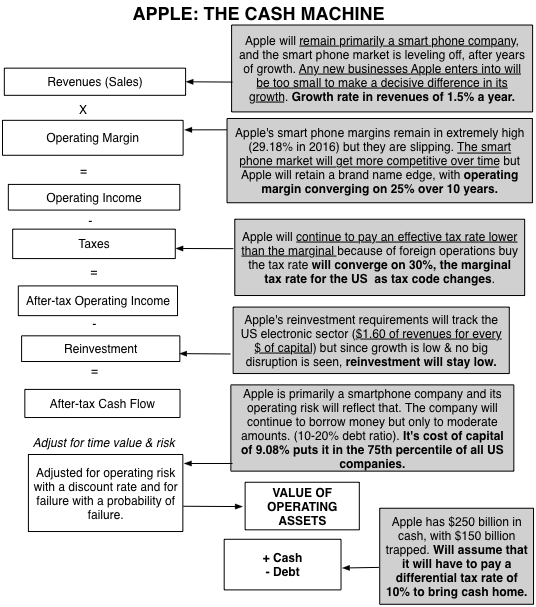
Some of you may find my story too cramped , seeing a greater possibility than I do of Apple breaking through into a new, big market (with Apple Pay or the Apple iCar). If you are in that group, please take my structure and make it yours, with a higher growth rate coming from your disruptive story, accompanied by lower margins and higher reinvestment. Others may find this story too optimistic, perhaps seeing a more precipitous fall of profit margins in the smart phone business and a greater tax liability from trapped cash. You too can alter the inputs to your liking and make your own judgment on Apple!
An Updated Valuation of Apple
Once you have a story for a company and convert that story into valuation inputs, the rest of the process becomes just mechanics. In the picture below, I have my February 2017 valuation of Apple.
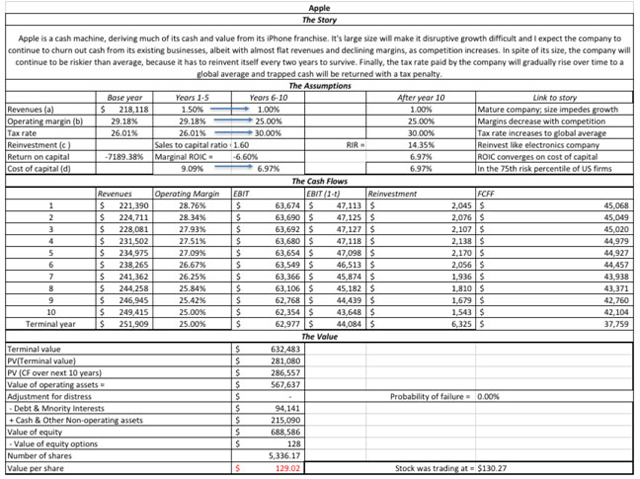
Download spreadsheet with valuation
Just as my valuation looked too optimistic a year, when the earnings report contained darker news, it may seem too pessimistic this year, after a much sunnier report. That said, it is worth emphasizing how much Apple is on the iPhone roller coaster ride, reporting better earnings in the quarters immediately after a new iPhone is released and much worse earnings in the quarters thereafter. While the market seems to want to go on a ride with Apple on its ups and downs, my fundamental story for Apple has barely shifted in the last few years and my valuations reflect that story stability.
Apple’s Price/Value Dynamics
I have taken my share of punishment on investments that have not gone well, with Valeant being a source of continuing pain (which I will return to after its next earnings report). Apple, though, has served me well in the last decade, but even with Apple, I have had extended periods where my faith has been tested. The picture below graphs Apple’s stock price from 2010 and 2017 with my valuations shown across time:
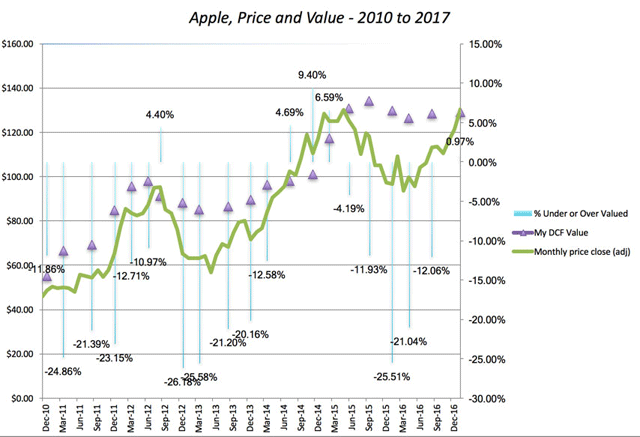
I held Apple from 2010 to 2012, as it traded under my estimated value. I sold in April 2012, just before a brief interlude where the price popped above value in June 2012, it reverted back to being under valued until June 2014. After spending a few months as an overvalued stock, the price plummeted in the late summer of 2015, making me a buyer, but it continued to drop until almost April 2016. It’s been a good ride since, and much as I want to attribute this to my valuation insights and brilliant timing, I have a sneaking suspicion that luck had just as much or perhaps more to do with it. Now that the stock is fully valued, decision time is fast approaching and I am ready with my sell trigger at $140/share, the outer end of the range that I have for Apple’s value today.
Conclusion
Apple is the greatest corporate cash machine in history and it is fully deserving of its market value. Its history as a disruptive force has led some investors to expect Apple to continue what it did a decade ago and come up with new products for new markets. Those expectations, though, don’t factor in the reality that as a much larger player with huge profit margins, Apple is more likely to be disrupted than be disruptor. Until investors learn to live with the company, as it exists now and not the company that they wish would exist in its place, there will continue to be mood swings in the market translating into the ebbs and flows of its stock price, and I hope to take advantage of them.






Leave a Reply