Floyd Norris, writing last Friday in the The New York Times, fretted about “The Chasm Between Consumers and the Fed.” We here at the Atlanta Fed share some of that concern, and indeed the Times article quotes from a speech by our president Dennis Lockhart on just that subject from last month. But then Norris takes a turn I didn’t expect. Norris’s Times article includes the following chart…
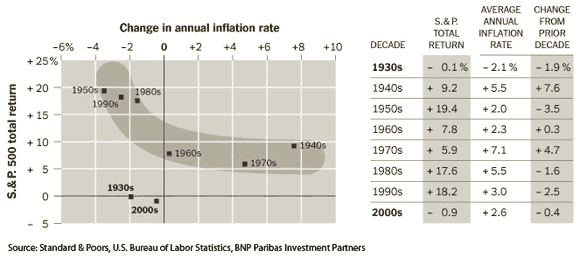
…and the article proceeds:
“The Fed’s goal is to keep the inflation rate at or near 2 percent, and it does not expect a significant increase for at least a few years. … The stock market is generally thought to do better when inflation is falling, but Martin Fridson, the global credit strategist for BNP Paribas Investment Partners, points out that is not always the case. There is, he says, a time when inflation is too low.
“The accompanying chart, based on a report by Mr. Fridson, shows that from the 1940s through the 1990s, there generally was a relationship. The more inflation declined in a decade from inflation in the previous decade, the better the stock market did.
“But in two decades, the 1930s and the first decade of this century, inflation fell from already low levels and the stock market suffered. ‘Below a certain level of inflation,’ Mr. Fridson said, ‘a further decline reflects economic weakness more than it reflects a salutary reining in of excessive monetary creation.’
“If that is correct, then it could be that both investors and those simply concerned with promoting economic growth should, as Mr. Fridson wrote, hope that Mr. Bernanke ‘fails in his stated goal of holding inflation to 2 percent or less.’ “
It was all good, up to that last paragraph. As President Lockhart reiterated in a speech today (emphasis added):
“I’ll explain the technical rationale of my Reserve Bank in supporting the scope of LSAP2 [the second round of large-scale asset purchases] last November.
“Through the summer and into the fall of last year, our internal forecasts at the Atlanta Fed were calling into question whether the policy stance at the time assured progress toward the committee’s growth and price stability objectives. In more normal times, these circumstances would have prompted a cut in the FOMC’s [Federal Open Market Committee] target for the federal funds rate. This approach would be (would have been) the prescription of the so-called Taylor rule which relates policy rate moves to forecast ‘misses’ on the Fed’s sustainable growth and stable inflation objectives.”
As we’ve argued in macroblog before, keeping inflation from falling below that “certain level of inflation” reflecting “economic weakness more than it reflects a salutary reining in of excessive monetary creation” was exactly what President Lockhart has offered in defense of implementing LSAP2, and in support of claims to its success.
There remain plenty of policy questions on which intelligent well-intentioned folk can disagree, but on the assertion that it is wise to guard against too much disinflation, we are in agreement. No need to find disagreements that aren’t really there.
- Bulenox: Get 45% to 91% OFF ... Use Discount Code: UNO
- Risk Our Money Not Yours | Get 50% to 90% OFF ... Use Discount Code: MMBVBKSM
Disclaimer: This page contains affiliate links. If you choose to make a purchase after clicking a link, we may receive a commission at no additional cost to you. Thank you for your support!




Leave a Reply