When we were young, we viewed our parents like they were the most powerful human beings in the world.
They exuded health, strength, such admirable quickness of mind in answering our endless questions, and the might to balance career and family.
How did they do it?
That used to puzzle us, as we kept getting delighted in the thought that we had extraordinary human beings playing the role of mom and dad.
That would seem to be the general line of thinking, until we reached early adulthood. A time that coincides with the period when we actually begin to notice the wrinkles developing on their faces, the thinning and graying hair, how their posture now seemingly well on its way to crunching over life’s heavy burdens.
At first, we begin to blame our society or the world in general for the wealth of new and challenging problems that people are forced to face everyday. Then, gradually we begin to realize that life for our parents after all, wasn’t as easy as we had perceived it when we were young.
As the years go by, with us having our own families, and going through the same stressful phases that our parents had gone through, it’s right then we start to realize that the weaknesses and diseases that came to plague our mom and dad would also be our unavoidable fate.
We’re all destined to grow old.
Today, the global anti-aging industry is worth more than $140 billion and has been predicted to rise to nearly $217 billion by 2021.
The world’s leading companies, including Google, are involved in anti-aging research and treatment of age-related diseases.
From Senescence Info, here’s a list of some of these companies and their anti-aging endeavors:
- ANTOXIS. A pre-clinical drug discovery company which focuses on the development of therapeutic antioxidants to treat age-related diseases that involve mitochondrial dysfunction e.g. Alzheimer’s disease.
- BIOMARKER PHARMACEUTICALS. With research largely based on DNA microarrays and caloric restriction, this company aims to develop pharmaceuticals and therapies to cure and delay the onset of diseases related to aging. This way, people will get to live better longer.
- BIOTIME. This company concentrates on the field of regenerative medicine, aiming to become a leader in the development of pluripotent stem cell-based technologies for the treatment of degenerative diseases.
- CALICO. Founded by Google’s parent company Alphabet Inc, aims to deepen man’s understanding of the biology which controls lifespan through advanced technologies. This knowledge will then guide them in coming up with interventions to help people lead longer and healthier lives.
- CENTAGEN. This company develops multi-path therapeutics for age-related disorders through rejuvenation of adult stem cells.
- CHRONOGEN. Worms have been the focus of this company’s research, and based their studies they aim to formulate drugs for the treatment of age-dependent diseases.
- CHRONOS THERAPEUTICS. This company is concerned in the treatment of age-related diseases particularly neurodegenerative disorders and osteoporosis by screening novel and repositioned drugs.
- ELIXIR PHARMACEUTICALS. This company has been conducting research in centenarians and model organism, e.g. yeast and Caenorhabditis elegans (a type of roundworm) to be able to formulate anti-aging products.
- GENECARE RESEARCH INSTITUTE. GRI’s research focus is on cancer and inflammation, but they have also taken interest in anti-aging.
- GENESCIENT. This is a biotechnology company which develops novel therapeutics to target chronic age-related diseases. They study and exploit the genetics of model animal and human whole genomes through evolutionary genomics that’s combined with massive selective screening.
- GERO. This company has developed omics data analysis methods for the identification of potential targets for therapeutic intervention against aging and age-related conditions.
- GERON. A clinical stage biopharmaceutical company with expertise in telomerase and telomere biology. They have formulated a telomerase inhibitor, imetelstat, which is already under clinical trial.
- HUMAN LONGEVITY, INC. (HLI). Among this company’s achievements is the creation of the world’s largest database of sequenced genomes and phenotypic (physical traits) data. With this endeavor, they are revolutionizing healthcare and aiming to make treatments more proactive, preventative, and personalized.
Now, what’s new?
The discovery, this time, is not about yeast, telomeres, stem cells, or genes.
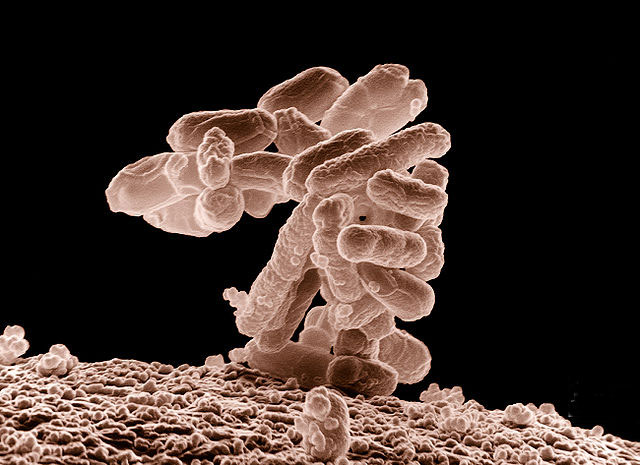
It’s about molecules. To be exact, a molecule type that’s produced by commensal bacteria and one which has the ability to extend healthspan.
Commensal bacteria are living organisms that derive their food from other living organisms. But, unlike parasites, they do not harm or hurt their host. This type of bacteria, also known as commensal microflora, usually inhabit the gut, respiratory tract, and skin.
In humans, the number of commensal bacteria that colonize our skin and mucosal surfaces is greater than the number of cells forming our body.
However, this molecule called “indole”, which was discovered by researchers at the Emory University School of Medicine, came from commensal bacteria that the team studied in the gut of worms (Caenorhabditis elegans), mice, and fruit flies to determine its anti-aging properties.
According to the authors, and as published on PNAS, the “small molecules [which are shown to be] produced by the microbiota and related to indole extend healthspan in geriatric worms, flies, and mice, without attendant effects on lifespan. Indoles act via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) and cause animals to retain a youthful gene expression profile. Indoles may represent a new class of therapeutics that improve the way we age as opposed to simply extending how long we live.”
Indoles and AHR are also found in the human body. The former exists in humans and mammals in small quantities, produced from plant dietary sources and intestinal microbiota. What’s more fascinating about indole is that it can extend not only an organism’s healthspan, but fecundity and reproductive span as well.
“The study is statistically extremely robust,” remarks Dario Valenzano of the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing. “The paper convincingly shows that the lack of indoles is detrimental to healthspan. What will be interesting is to see if the same effect holds good with wild-type animals treated [extraneously] with indoles.”
Indeed, it’s a remarkable discovery. But, mankind appears to unfortunately, still have a long way to go in their quest for longer, healthier life.
As study author Daniel Kalman notes: “It is a long road to go from the data we present to a drug. That takes careful development, testing, and safety and efficacy trials.”
Despite the relatively long road ahead (I say ‘relatively’ based on the fact that AI applications are on a seemingly rapid upward trajectory and anything is possible. We may have a breakthrough tomorrow or five years from, nobody knows for sure) the fact that new advancements in modern technology are finally offering up some real promising possibilities for ways to reverse aging as a process, is a breakthrough in anti-aging research and the right step toward a healthier, longer life and consequently, a brighter future for all of us.




Totally outdated list of companies – only Calico and HLI are really operational. Most of the others are closed, and others are on life-support.