Last week the ECB announced new monetary policy actions to help restore growth in the Euro area and bring inflation closer to its 2% target. Interest rates were reduced and further provision of loans to commercial banks were announced. In addition, there is a plan to implement purchases of asset based securities.
The effectiveness of recent monetary policy actions by central banks has been met with some skepticism because it does not deliver the necessary increase in lending to the private sector. While liquidity is introduced, it seems to get stuck in the accounts that the commercial banks hold at the central bank (reserves). Because of this, both the Bank of England and now the ECB are implementing injections of liquidity that are linked to increased lending to the private sector by the financial institutions that are borrowing that liquidity.
The role that reserves play in the recent monetary policy actions by the ECB leads some times to confusion. Some seem to think that the high level of reserves that banks hold is a measure of the failure of central banks to generate additional loans to the private sector. The logic is that reserves stay high because of the lack of willingness to lend. This is the wrong view of reserves, they cannot simply be seen as resources that are waiting to be provided as loans to the private sector.
Reserves are a liability in the central bank balance sheet that it is created when the central bank decides to allocate more loans to commercial banks or when it decides to buy securities. If a commercial bank decides to give a loan to one of its customer (household or business), the reserves do not disappear. Once that customer uses its loan for a purchase, these reserves are transferred from one commercial bank to another, but the level of reserves remains constant.
How can reserves go down? In the case of the ECB, most of the injections in liquidity have been done via loans to commercial banks. Reserves will only go down when commercial banks pay back their loans with the central bank (or when the central bank decides to reduce the amount of loans it provides as some of the outstanding ones are repaid). So any increase in the provision of loans by the ECB will lead to an increase in reserves. Below are the two series: loans to commercial banks (an asset for the ECB) and reserves of commercial banks at the ECB (a liability at the ECB). Both series are in Billions of Euros (Source: ECB).
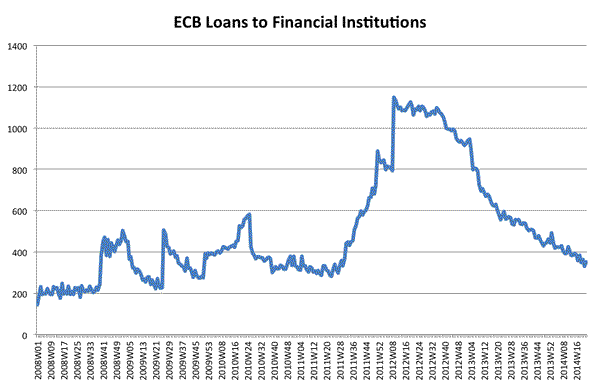
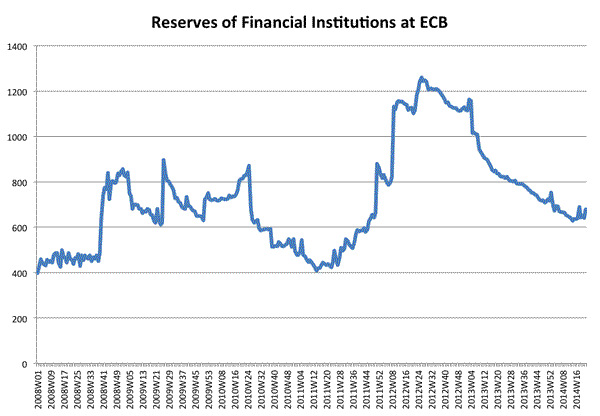
The evolution of both series is identical. The large increase in loans (LTROs) that started in the Fall of 2011 led to a large increase in reserves. Since then, both series have been coming down as Euro commercial banks have been repaying their loans (voluntarily). So the balance sheet of the ECB has been shrinking dramatically over the last months. The new wave of loans announced by Mario Draghi is likely to increase both series again (although by how much will depend on how Euro financial institutions feel the need to tap into additional ECB funding).
The fact that the two series move together does not mean that the actions of the central bank are ineffective. It is possible that the availability of funding for some banks leads them to provide more loans to the private sector. What one cannot do is judge the success of these actions by the level of reserves in the financial system. The level of reserves will not change when the private loans are given.
As a point of comparison, the profile of the series above for the US Federal Reserve is very different: they keep trending up, no decrease at all. The reason is that the US central bank has increased its balance sheet by buying securities. So reserves are created agains the purchase of those securities. In this case, the level of reserves is even more directly linked to the actions of the central bank. It is only when the central bank decides to sell those securities that the level of reserves will come down. And this is the new step that Draghi has promised in his press conference last week, the ECB is willing to engage in true quantitative easing via the purchase of asset based securities.
- Bulenox: Get 45% to 91% OFF ... Use Discount Code: UNO
- Risk Our Money Not Yours | Get 50% to 90% OFF ... Use Discount Code: MMBVBKSM
Disclaimer: This page contains affiliate links. If you choose to make a purchase after clicking a link, we may receive a commission at no additional cost to you. Thank you for your support!


Leave a Reply