This is a question that observers, particularly those who are skeptical of the aggregate demand-shortfall view, often raise. Ryan Avent and Paul Krugman both answer this question in recent posts. Here is Avent:
The answer to the question of why deflation in, say, America hasn’t been sustained despite little progress closing the output gap is extremely simple: the Fed has been determined not to allow that to happen…What the record shows is that disinflation below 2% inflation prompts aggressive Fed reactions, which are generally successful at reversing inflation expectations. The critical difference between the Depression and the Great Recession was that Great-Recession-era central banks were determined to avert deflation and where willing to prop up the financial system, drop rates to zero, and engage in unconventional policy in order to keep inflation positive.
I think that assessment is largely correct. The only part I would add is that once FDR took the reigns of monetary policy in 1933 (by breaking the link between the dollar and gold and not sterilizing gold inflows) inflation emerged and coincided with a large output. Though the Fed didn’t cause this inflation, the Fed tolerated it until 1937 as seen in the figure below:
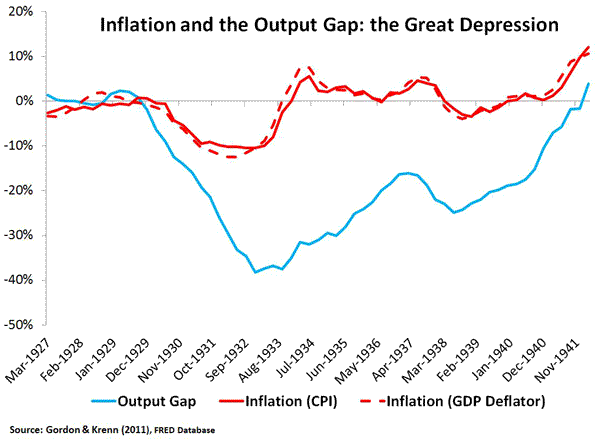
As Paul Krugman notes, this bout of inflation between 1933 and 1937 was not that different from what we have today as seen in the chart below.
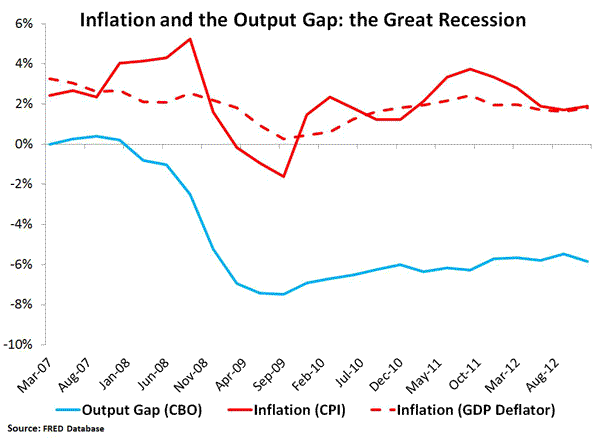
Below is a table that compares the output gaps and inflation rates that occurred after the troughs of 1933 and 2009. Again, we see that inflation rates were not that different.
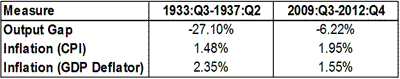
The only big difference between the periods is the output gaps. The mid-1930s output gap was far larger than the current one and yet that period had a similarly-sized rate of inflation. For me, then, the interesting question is why has inflation during the last two largest U.S. economic crisis been similar? Why were they both gravitating around 2%? Ryan Avent has an answer that I suspect is true to some extent for both periods:
[T]he Fed’s observed success in averting deflation should lead one to ask whether its control over inflation expectations suddenly evaporates once those expectations hit 2%. My view is that it does not—why should it, after all?—and that the main constraint on a faster economic recovery is the Fed’s reluctance to push inflation over 2%.
This makes a lot of sense for the 1930s too since it is well documented the Fed was concerned about inflation getting too high during this time. There were a few years of higher-than-normal inflation, but the average inflation rate was kept in line by the Fed. Even at the expense of creating a recession in 1937-1938. History repeats itself.
Disclaimer: This page contains affiliate links. If you choose to make a purchase after clicking a link, we may receive a commission at no additional cost to you. Thank you for your support!



Leave a Reply